Single Line Diagram
Understanding the electrical distribution system of a full electric vessel
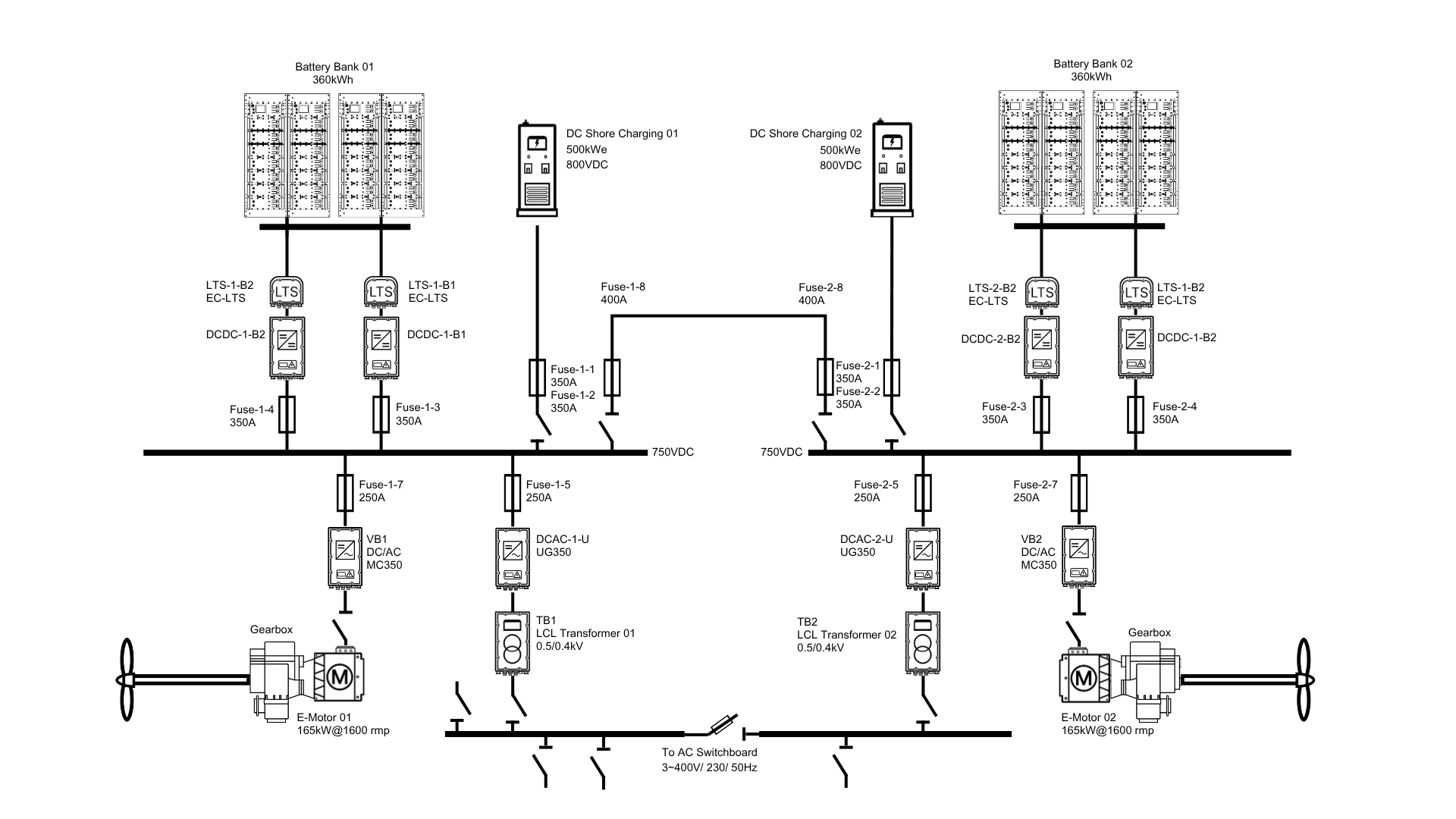
System Configuration
This Single Line Diagram illustrates our dual redundant marine electric propulsion system. Two 360kWh battery banks power twin 165kW electric motors through a sophisticated power management network. The system features 500kWe shore charging stations operating at 800VDC, multiple DCDC converters maintaining 750VDC on the main bus, and comprehensive protection through strategically placed fuses. DCAC inverters convert power for the vessel's 3-400V/230V AC systems. This symmetrical architecture ensures reliability—if one side fails, the other maintains operation. The design prioritizes redundancy, safety, and efficient power distribution for optimal marine performance in all conditions.